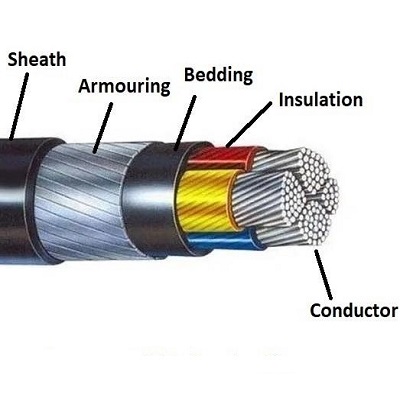
Why can’t high-voltage cables be buried underground?
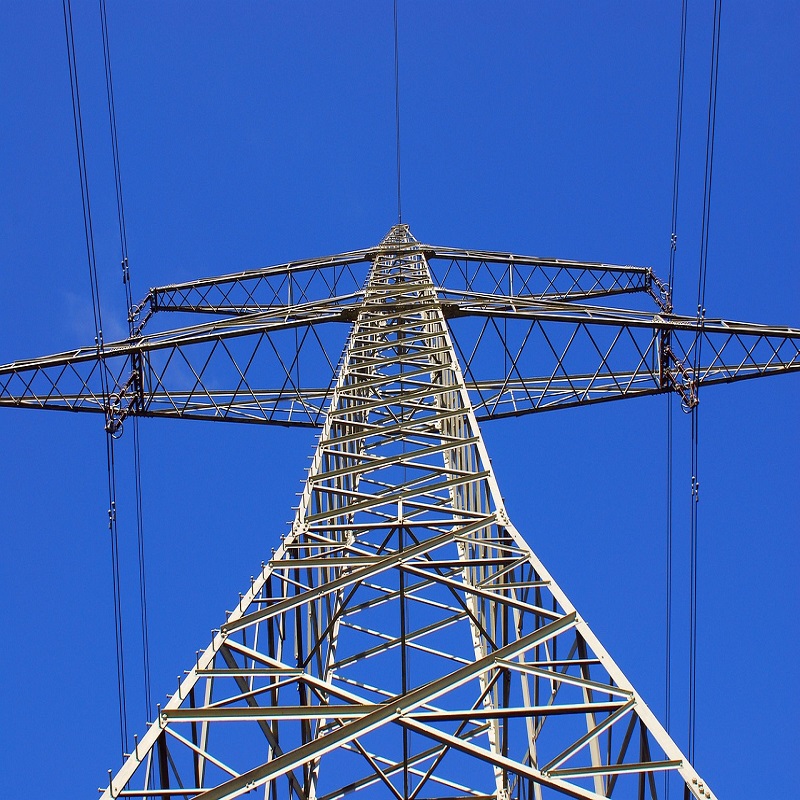

High-voltage cables are an essential part of our modern electrical infrastructure, transporting large amounts of electricity over long distances. While many cables are buried underground for safety and aesthetic reasons, high voltage cables are generally not buried underground due to various technical and practical challenges.
One of the main reasons why high voltage cables are not buried underground is due to heat dissipation issues. When high-voltage current flows through a cable, heat is generated. This heat needs to be dissipated to prevent the cable from overheating and potentially causing a fire or damaging the insulation. When cables are buried underground, the surrounding soil acts as an insulator, making it difficult for heat to dissipate effectively. This can cause the cable's operating temperature to rise significantly, reducing its efficiency and service life.
Another factor to consider is the maintenance and repair of high-voltage cables. When cables are buried underground, it can be challenging and costly to perform routine maintenance or troubleshoot when a fault occurs. Unlike low-voltage cables, high-voltage cables require specialized equipment and expertise to repair, and the repair process becomes more complicated when the cables are buried underground. This could lead to prolonged power outages and increase costs for utilities and consumers.
In addition, the cost of buried high-voltage cables is significantly higher than that of overhead installations. Excavation, specialized insulation and additional safety measures can all contribute to increased underground installation costs. This cost factor often makes overhead installation a more practical and cost-effective option for high-voltage cables.
While burying high-voltage cables underground may offer some benefits, such as reduced visual impact and increased protection against weather-related damage, technical and practical challenges related to heat dissipation, maintenance and cost make overhead installations the preferred choice for high-voltage transmission lines. As technology continues to advance, new solutions may emerge to address these challenges, but for now, overhead installation remains the most viable option for high-voltage cables.